分享到
Quantitative trait loci associated with catechins content in tea plant
Catechins, a group of flavonoids, are one of the most important secondary metabolite of tea plant (Camellia sinensis), known to possess a wide variety of pharmacological activities including antioxidant and free-radical-scavenging effects, which is believed to be the underlying protective mechanism primarily responsible for the health benefits of tea. And the content and composition of catechins in the tender tea shoots is also the major determinant of processing suitability of tea cultivars and quality properties of made tea. The issue of improving the content and composition of tea catechins has become increasingly important in tea plant breeding programs, however, the genetic basis of related traits remains poorly understood.
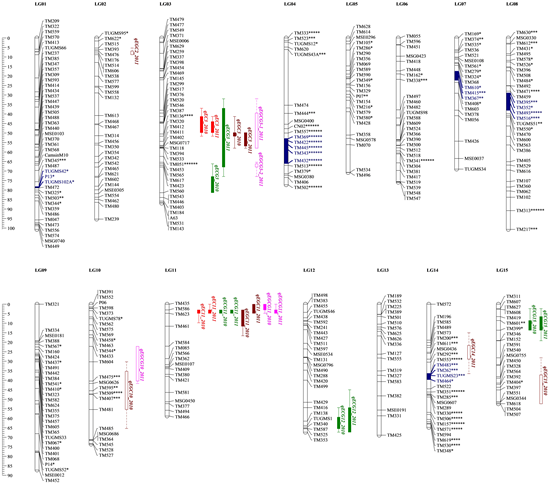
Recently, researchers from the Tea Research Institute (TRI) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) have made a major progress on the genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling catechins content in tea plant. The researchers firstly developed a mapping population consisting of 183 F1 progenies by an inter-varietal cross between two C. sinensis varieties with diverse catechins composition. According to the two-way pseudo-testcross mapping strategy, a relatively saturated genetic map was subsequently constructed using 406 SSR markers, with an average locus spacing of 2.9 cM. And finally, twenty-five QTLs associated with catechins content were identified on seven linkage groups. Of these, nine stable QTLs were validated across years. The population variability explained by each QTL was predominantly at moderate-to-high levels, and ranged from 2.4% to 71.0%. This is the first report on the identification of QTL for catechins content in tea plant. The results of this study provide a foundation for further cloning and functional characterization of catechin QTLs for utilization in improvement of tea plant.
This work is partially supported by the China Agriculture Research System Project (CARS-023) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (31170624). The research result was published in PLoS ONE 2014, 9(3): e93131. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093131.

Recently, researchers from the Tea Research Institute (TRI) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) have made a major progress on the genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling catechins content in tea plant. The researchers firstly developed a mapping population consisting of 183 F1 progenies by an inter-varietal cross between two C. sinensis varieties with diverse catechins composition. According to the two-way pseudo-testcross mapping strategy, a relatively saturated genetic map was subsequently constructed using 406 SSR markers, with an average locus spacing of 2.9 cM. And finally, twenty-five QTLs associated with catechins content were identified on seven linkage groups. Of these, nine stable QTLs were validated across years. The population variability explained by each QTL was predominantly at moderate-to-high levels, and ranged from 2.4% to 71.0%. This is the first report on the identification of QTL for catechins content in tea plant. The results of this study provide a foundation for further cloning and functional characterization of catechin QTLs for utilization in improvement of tea plant.
This work is partially supported by the China Agriculture Research System Project (CARS-023) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (31170624). The research result was published in PLoS ONE 2014, 9(3): e93131. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093131.
Latest News
-
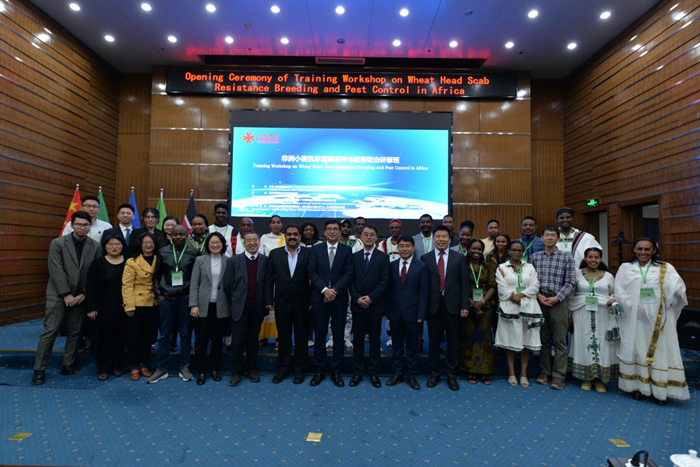 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
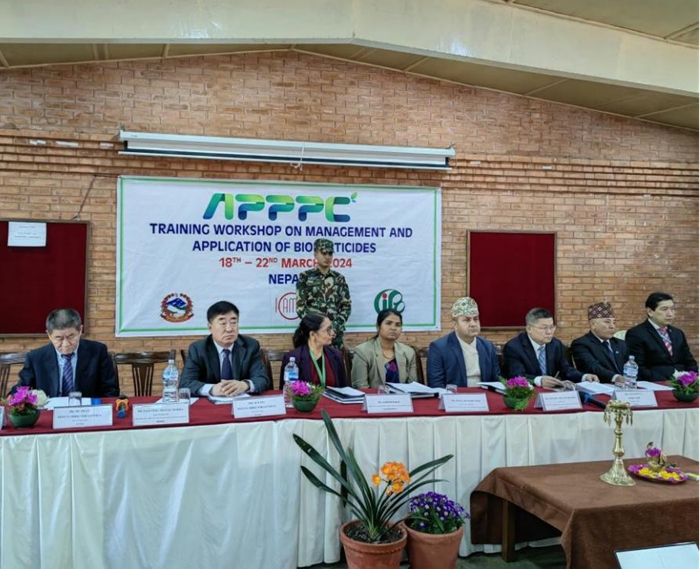 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
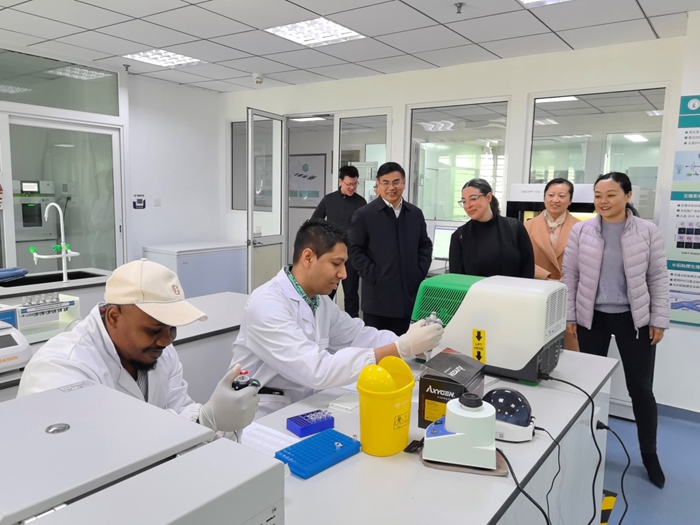 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
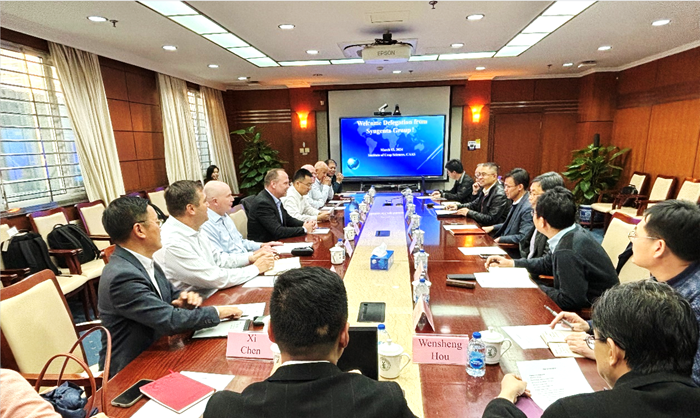 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
