Researchers from IFST-CAAS developed the preparation technology of superior quality and high resistant rice noodles with modified rice noodles and psyllium fiber
Recently, the Food Nutrition and Functional Food Innovation Team of the Institute of Food Science and Technology of CAAS used modified rice flour (RF) and psyllium fiber to prepare high resistant rice noodles. This work was published in the top journal International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (JCR Q1, IF=8.2).
Rice noodles are popular among consumers due to their smooth texture, nutritional value, and delicious taste. However, traditional fresh rice noodles are classified as high glycemic index (GI) (GI value > 70) foods because of its high content of rapidly digestible starch (RDS). Prolonged consumption of such noodles may not be suitable for individuals with obesity or type II diabetes.
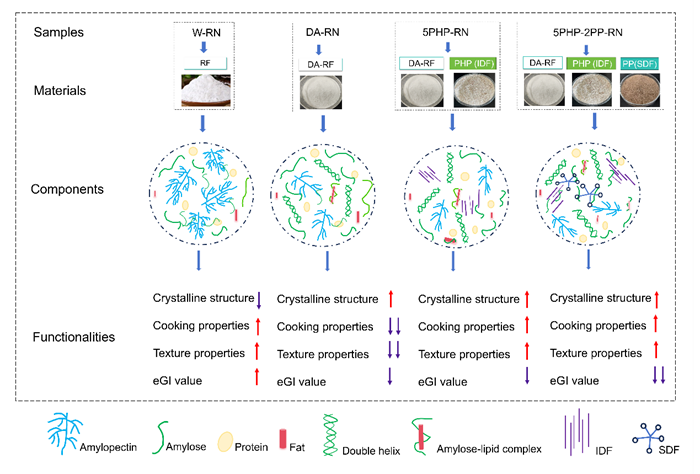
An effective strategy to reduce the starch digestibility of rice noodles involves increasing the content of resistant starch (RS) in RF and using it as the primary processing material. Studies have shown that rice noodles made with RF containing high RS content exhibit significantly lower digestibility. However, these noodles often suffer from high breakage rates, poor taste, and inferior edible quality.
Psyllium fiber is recognized as an important natural functional polysaccharide for enhancing the quality of starch-based foods. Interestingly, psyllium seed husk powder (PHP) is rich in insoluble dietary fiber (IDF), whereas psyllium seed powder (PP) contains higher levels of soluble dietary fiber (SDF). Both natural PHP and PP have higher viscosity compared to extracted polysaccharides.
This study aims to use high RS content RF as the main raw material for preparing rice noodles to reduce their GI value, and to enhance the food quality of these noodles by incorporating natural PHP and PP. The goal is to create high RS rice noodles that are not only nutritious but also have improved taste and functional properties. Results indicated that rice noodles prepared with high RS content RF solely had poor eating quality. PHP effectively enhanced the cooking properties and texture quality of high RS rice noodles, while PP further reduced the RDS content and starch digestibility. The study found that both 5PHP-RN (eGI=66.74) and 5PHP-2PP-RN (eGI=65.77) could be classified as medium-GI foods. Moreover, the addition of PHP and PP to the rice noodle ingredients did not significantly alter its flavor.
This study offers an important approach to improve the eating quality of high RS content rice noodles and provides healthier staple food options for obesity and diabetes individuals.
Professor Fengzhong Wang and Litao Tong are corresponding authors and the master student Xue Gong is the first author. This study was supported by the "Tianshan Talents" Training Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2022TSYCCX0063) and the Yi-Hai Kerry Golden Dragon Fish Innovation Funding.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132779
-
 Aug 22, 2024Seminar on Grassland Protection and Sustainable Livestock Development for BRI Partner Countries has kicked off in Hohhot
Aug 22, 2024Seminar on Grassland Protection and Sustainable Livestock Development for BRI Partner Countries has kicked off in Hohhot -
 Aug 01, 2024Deputy Prime Minister of Cuba Visited IVF-CAAS
Aug 01, 2024Deputy Prime Minister of Cuba Visited IVF-CAAS -
 Aug 01, 2024CAAS Vice President Visits Africa
Aug 01, 2024CAAS Vice President Visits Africa -
 Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS
Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS -
 Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha
Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha
