分享到
OsELF3-2, an ortholog of Arabidopsis ELF3, interacts with the E3 ligase APIP6 and negatively regulates immunity against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice
Rice blast, which is caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae, significantly reduces rice yield in most rice-growing areas. Although many studies have shown that the ubiquitin E3 ligases play an important role in the regulation of blast resistance in rice, the function of their substrates in immune responses is still not fully understood. Recently, researchers at State Key Laboratory for Biology of Plant Diseases and Insect Pests, Institute of Plant Protection (IPP), CAAS, have published a research paper about E3 ligase APIP6 substrate protein OsELF3-2 in rice.
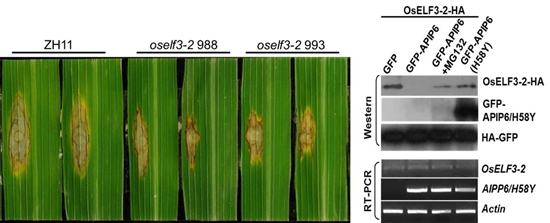
OsELF3-2 plays a negative role in blast resistance and is degraded by APIP6-mediated ubiquitination pathway

OsELF3-2 plays a negative role in blast resistance and is degraded by APIP6-mediated ubiquitination pathway
They previously demonstrated that fungal effector AvrPiz-t in M. oryzae suppresses PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI) by targeting the rice RING E3 ligase APIP6 for degradation. However, the APIP6 substrates in immune responses remain unclear.
In this paper, they found that APIP6 interacts with OsELF3-2 (Homolog of Arabidopsis ELF3) in vitro and in vivo. Compared with the wild type, the oself3-2 mutant and RNAi plants leads to a significant increase of flg22- and chitin-induced ROS generation, and enhanced resistance to compatible a M. oryzae isolate. Co-expression assays in rice protoplasts and N. benthamiana leaves indicate that APIP6 can promote OsELF3-2 degradation and the degradation can be inhibited by MG132. Take together; these results demonstrate that OsELF3-2 plays a negative role in PTI and is regulated by the APIP6-mediated ubiquitination pathway in rice.
More details are available on the bellow links:
http://www.cell.com/molecular-plant/abstract/S1674-2052(15)00327-5
In this paper, they found that APIP6 interacts with OsELF3-2 (Homolog of Arabidopsis ELF3) in vitro and in vivo. Compared with the wild type, the oself3-2 mutant and RNAi plants leads to a significant increase of flg22- and chitin-induced ROS generation, and enhanced resistance to compatible a M. oryzae isolate. Co-expression assays in rice protoplasts and N. benthamiana leaves indicate that APIP6 can promote OsELF3-2 degradation and the degradation can be inhibited by MG132. Take together; these results demonstrate that OsELF3-2 plays a negative role in PTI and is regulated by the APIP6-mediated ubiquitination pathway in rice.
More details are available on the bellow links:
http://www.cell.com/molecular-plant/abstract/S1674-2052(15)00327-5
Latest News
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
