New perspectives on high-value utilization of cotton stalks boost sustainable development of the cotton industry
A recent paper by Prof. Fuguang Li's team from the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) has conducted an in-depth review of the latest advancements in high-value utilization of cotton stalks, laying the foundation for sustainable development in the cotton industry. The article, titled “Cotton stalk valorization towards bio-based materials, chemicals, and biofuels: A review” published in the prestigious "Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews" journal (IF=15.9), provides strategic guidance and practical insights crucial for the industrialization of cotton stalk utilization.
In 2023, China's cotton production reached 5.618 million tons, generating approximately 28 million tons of cotton stalks with a grain-to-straw ratio of 1:5. Currently, these stalks are mainly disposed of through field return or burning, resulting in resource waste and environmental degradation. Therefore, their high-value utilization is vital for promoting a circular economy and reducing agricultural carbon emissions.
Cotton stalks, rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, offer significant potential for bio-based materials, chemicals, and biofuels. However, limited research exists on their specific properties and transformation challenges. This study extensively explored their chemical structure and distinctive features, including high cellulose content, fiber spinnability, good mechanical strength, high recalcitrance, and high calorific value.
The research delved into advancements in converting cotton stalks into bio-based materials, chemicals, and biofuels. Optimized strategies were suggested by comparing various conversion methods, such as using stalks for bio-based board production, manufacturing cellulose-based materials from bark, and synthesizing biofuels via thermochemical conversion. Economic and technical analyses of diverse conversion cases were undertaken, offering a multi-product co-production approach to enhance the economic viability of cotton stalk valorization.
Furthermore, the study proposed innovative strategies to overcome the recalcitrance challenges of cotton stalks. These include adopting "lignin-first" biorefinery approaches, manipulating lignin synthesis in cotton plants, and targeted utilization of specific stalk components. The resulting insights offer promising avenues for the efficient and profitable utilization of cotton stalks.
The research, led by co-first authors Dr. Chenggu Cai and Dr. Zhanbiao Wang, and corresponding author Prof. Fuguang Li, and other contributing authors including Prof. Lei Ma of CAAS, Assoc. Prof. Zhaoxian Xu from Nanjing University of Science and Technology, and Dr. Jianming Yu from Sinopec Maoming Company. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Science and Technology Innovation Project of CAAS.
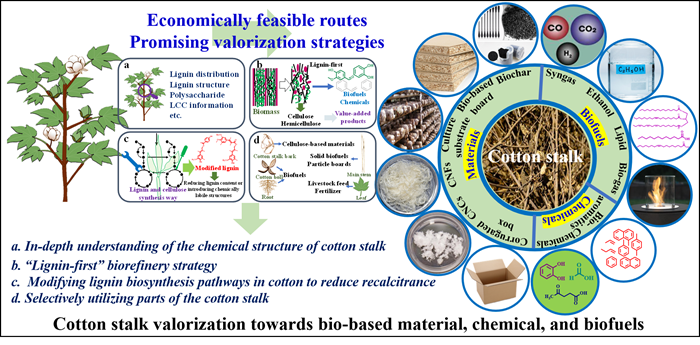
Fig. 1. The graphical abstract of cotton stalk valorization towards bio-based materials. chemicals, and biofuels
By. Chenggu Cai (caichenggu@caas.cn)
-
 Jun 28, 2024A cigar tobacco QX208, with excellent quality, disease and cold resistance, passed field evaluation
Jun 28, 2024A cigar tobacco QX208, with excellent quality, disease and cold resistance, passed field evaluation -
 Jun 18, 2024Visit by CGIAR Executive Director Ismahane Elouafi to the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers,CAAS
Jun 18, 2024Visit by CGIAR Executive Director Ismahane Elouafi to the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers,CAAS -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Deputy Director General of IAEA
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Deputy Director General of IAEA -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Chairman of the Understanding China Forum
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Chairman of the Understanding China Forum -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Greek Minister
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Greek Minister
