Scientists from IBFC CAAS reveal the antiobesity effects of melatonin by meta-analysis and machine learning
Researchers of the innovative team for development and utilization of functional feed in the south China from the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, systematically studied exogenous administration of melatonin significantly reduced body and improved lipid metabolism via meta-analysis and machine learning, and these results were to some extent dependent on factors such as melatonin dosage, initial body weight, and treatment duration.
Excess energy intake is stored in white adipose tissue, leading to increased body weight and the occurrence of obesity. Obesity and its related metabolic disorders are the most common and harmful diseases, resulting in decreased quality of life and increased incidence of morbidity and mortality. The consumption of a high-calorie diet such as a high-fat and high-sugar diets, and alterations in lifestyle, such as nocturnal activities, lead to biological rhythm and metabolic disorders, resulting in metabolic syndromes such as obesity, type-2 diabetes and stroke. Therefore, regulating circadian rhythms and metabolism of fat and glucose by reducing the intake of high-calorie diets and utilizing potential therapeutic agents such as amino acids, melatonin, and probiotics may become a possible treatment method for alleviating the current occurrence of obesity.
The research team developed a meta-analysis and machine learning study to evaluate the antiobesity effect of melatonin on obese mice or rats. Melatonin significantly reduced body weight, serum GLU, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, and cholesterol levels in obese mice or rats. Meta-regression analysis and machine learning indicated that the dosage of melatonin is the primary factor influencing body weight, with higher melatonin dosages leading to a stronger weight reduction effect. Together, male obese C57BL/6 mice and Sprague-Dawley rats with an IBW of 100-200 g showed better body weight reduction when supplemented with a dose of 10-30 mg/kg melatonin administered at night via injection for 5-8 weeks.
The research was funded by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1610242022001-02; 1610242023002), Natural Science Foundation of Changsha Municipal (kq2208249), Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project Special Fund of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (ASTIP-IBFC), National Key R&D Program of China (No.2021YFD1300402) and TaiShan Industrial Experts Program (tscy20190121).
The study entitled Meta-analysis and machine learning reveal the antiobesity effects of melatonin on obese rodents has been published online in Obesity Reviews journal and can be accessed through the following link http://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13701.
Fig. Funnel plots and Egger's test assessing the publication bias
By Li Yuying&Shi Pengjun
(liyuying01@caas.cn)
-
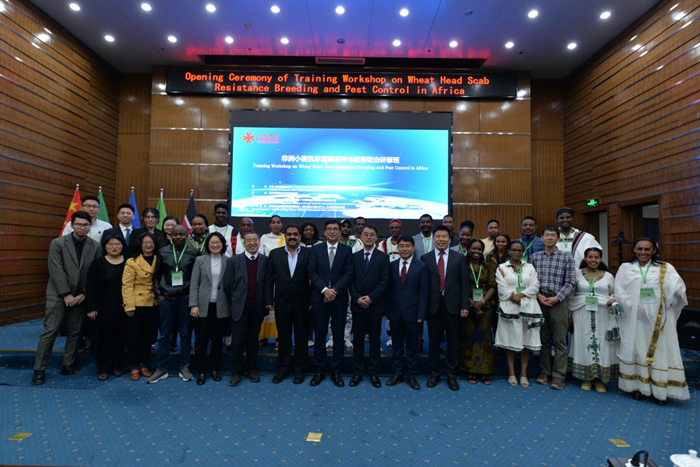 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
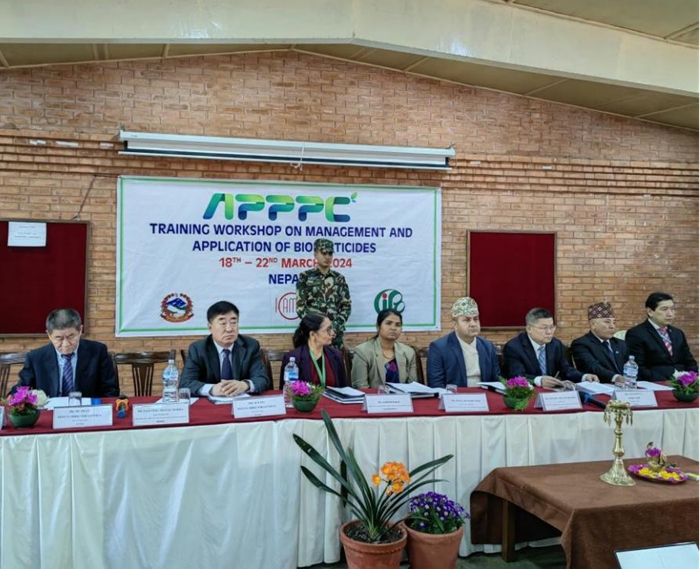 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
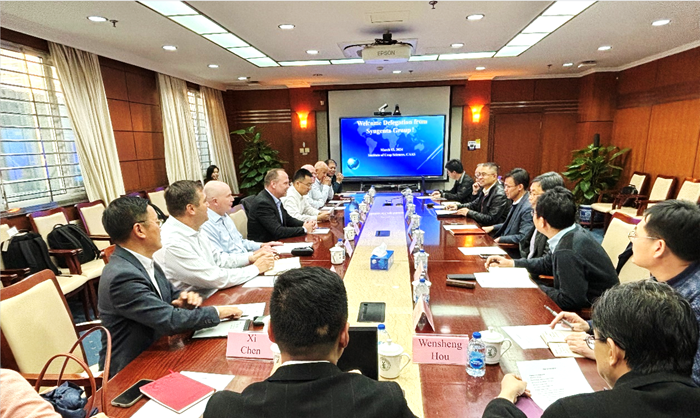 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
