分享到
SLMBP21 is required for tomato AZ development
The research team led by Dr. Mao Long at Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS), CAAS discovered a new MADS-box transcription factor that was responsible for tomato fruit abscission zone (AZ) development. This group used yeast two-hybrid system to find the MADS-box protein SLMBP21 can interact with two previously identified MADS-box proteins JOINTLESS (J) and MACROCAYLYX (MC) that are also implicated in AZ development. SLMBP21 was confirmed to be required for AZ development by a transgenic approach.
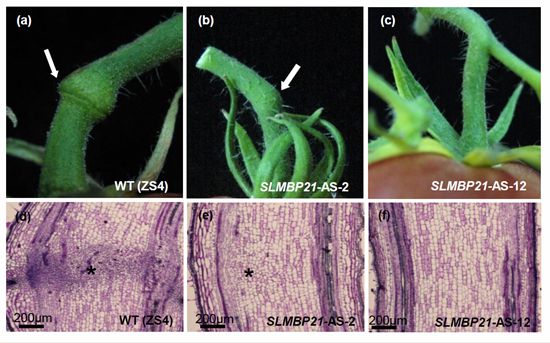
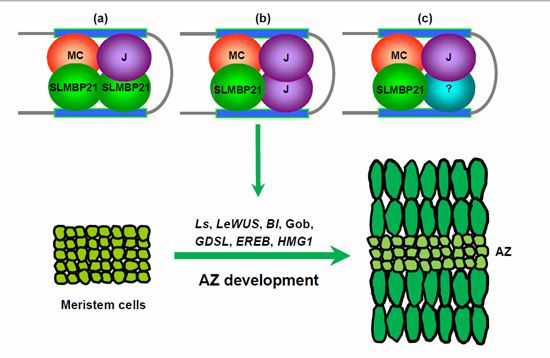

The work further showed that SLMBP21, J, and MC could readily form higher order protein complexes in which SLMBP21 plays a key role as a transcription activator. Because SLMBP21 belongs to the FBP9/23 subclade of the SEP gene family, which is absent in the model plant Arabidopsis, the SLMBP21-J-MC complex may represent a distinct mechanism for plant AZ development. This discovery should assist scientists to generate new types of tomatoes with increased yield due to reduced loss and for improved mechanical harvesting.

The results were published online on the interactional journal The Plant Journal.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/tpj.12387/abstract
The work is supported by National Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/tpj.12387/abstract
The work is supported by National Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Latest News
-
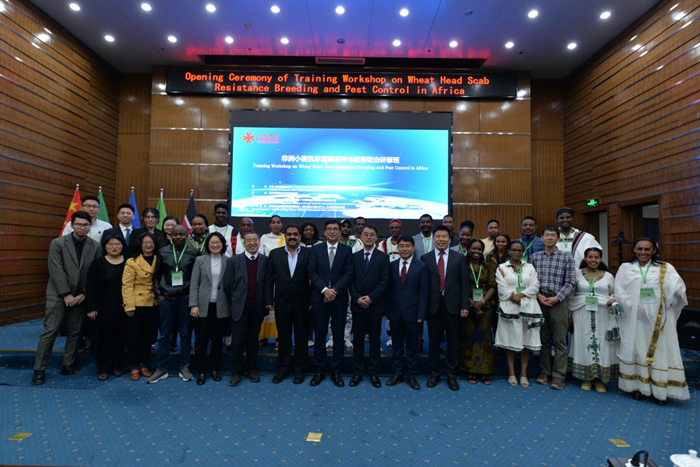 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
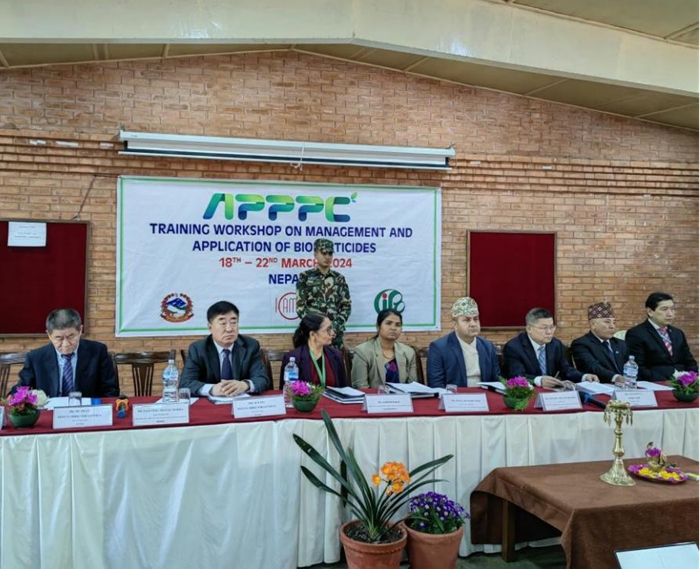 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
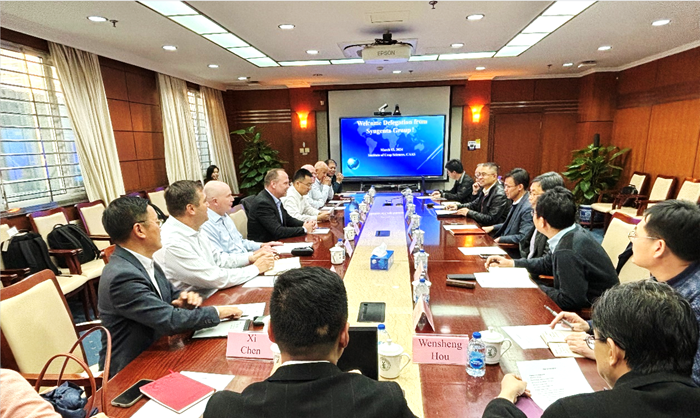 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
