Salt stress reduces photosynthetic oscillations in tomato under dynamic light intensity
Recently, the Plant Environmental Engineering of Protected Agriculture Team from the Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences made new progress, revealing the mechanism by which salt stress regulates the dynamic photosynthesis of tomato through triose phosphate utilization (TPU) and stomata under high CO2 partial pressure. The related findings have been published in the Journal of Experimental Botany .
Salt stress is one of the abiotic stresses to which plants are often subjected in nature and in agricultural production. Meanwhile, due to factors such as continuous changes in the solar elevation angle, canopy shade and cloud movement, dynamic changes in light are ubiquitous. Salt stress is usually accompanied by dynamic light intensity, and the two together affect the light energy utilization and growth of crops. This study found that under high CO2 partial pressure, rapid increases in light intensity caused profound photosynthetic oscillations in the photosynthetic rate of tomato leaves. Short-term salt stress may reduce the photosynthetic oscillations caused by dynamic light intensity under high CO2 partial pressure by increasing TPU capacity and at the same time increasing stomatal limitation to reduce CO2 partial pressure in the mesophyll cell. This study provides a theoretical basis for systematically analyzing the effects of salt stress on plant photosynthesis, and cultivating crop varieties of high photosynthetic efficiency on the saline land.
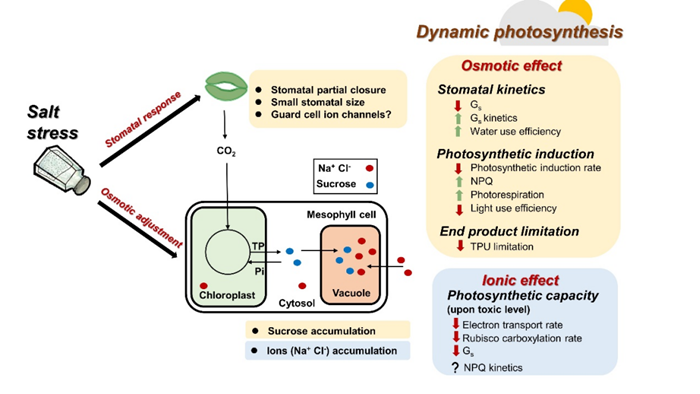
Effects of salt stress on dynamic photosynthesis
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program of China Association for Science and Technology, and Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund.
Linkage: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erae089
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
