分享到
FRI Wins the Second Prize of 2014 National Science & Technology Progress Award by "Creation of New-type Enzyme Feed Additives"
Recently, the 2014 National Science and Technology Progress Award announced through public appraisal. The project "Creation of New-type Enzyme Feed Additives" conducted by Professor Yao Bin’s group of Feed Research Institute (FRI), CAAS won the second prize.

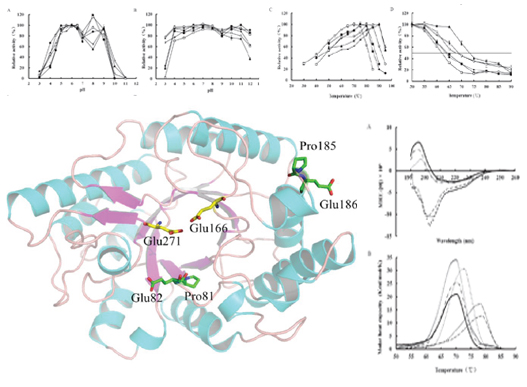

Dr. Yao’s team has been spending more than 20 years to apply techniques of molecular biology, proteomics, bioinformatics, etc. to overcome the feed enzyme-related bottlenecks in China, including enzyme performance, production cost, property rights and patents, and sustainable development. This finding has cloned more than 100 novel genes (xlanase, glucanase, mannannase, α-galactosidase, etc.), which provides application potentials in feed industry. The research also set up a new protein engineering system to improve enzyme performance, and produced enzymes in a cost-effective, high-yield expression system (the yield up to 10-50 g/l). Their new apply techniques broke down the patent-related barriers set by developed countries and played a leading role in mining and utilization of genetic resources. As results, Dr. Yao’s team has improved the production and preparation efficiency of feed enzyme technology system, which could achieve cost-effective industrialization and extension of feed enzymes. Their apply techniques made great contributions to the rapid development of feed industry in China.

The project achievements have been extensively applied in China feed industry. Since 2011, the production and sales of single and compound enzyme products by domestic feed industries have reached more than 200,000 tons, and the products have been exported to Europe and the United States. Over 80% domestic animal feed contains the project-related enzymes. It’s estimated that 50 million tons of feed grains and 10 million tons of phosphorus resources have been saved, and the discharge of phosphorus and nitrogen pollution, approximately 13million tons, have been reduced.
The scientific achievements of this project include 66 authorized patents (including 2 PAT), 113 SCI papers, 9 industrial standards, and close collaboration with more than 20 domestic top enzyme companies on industrialization and technology transfer.
The scientific achievements of this project include 66 authorized patents (including 2 PAT), 113 SCI papers, 9 industrial standards, and close collaboration with more than 20 domestic top enzyme companies on industrialization and technology transfer.
By MA Rui
marui@caas.cn
marui@caas.cn
Latest News
-
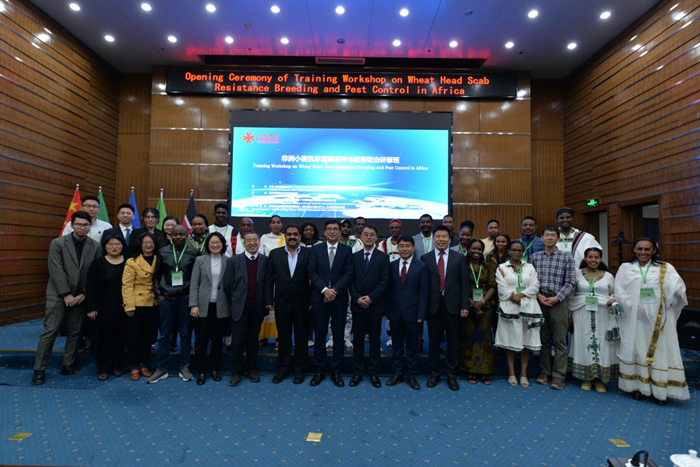 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
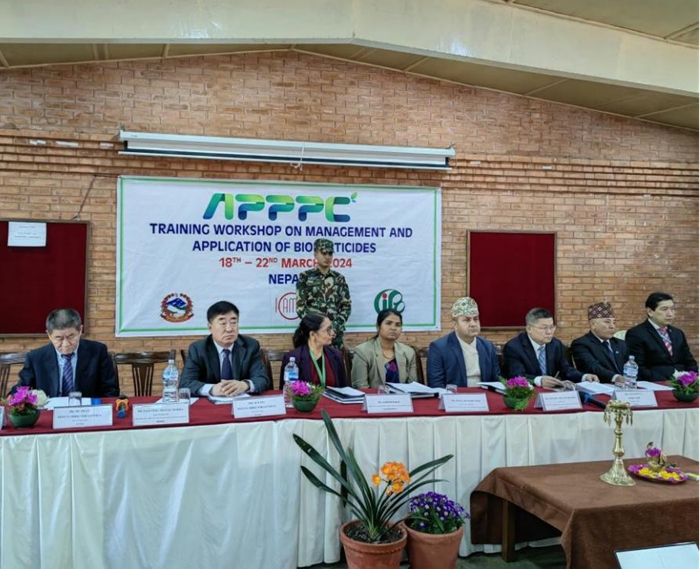 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
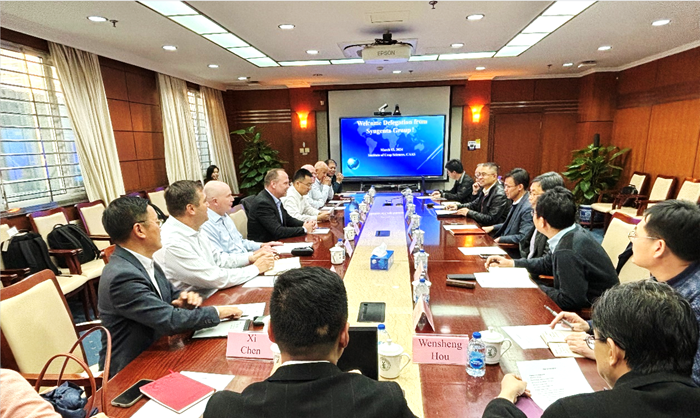 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
