Identification of a key gene that regulates the negative correlation between cotton yield and fiber quality
Recently, a paper entitled “Genetic linkage analysis of stable QTLs in Gossypium hirsutum RIL population revealed function of GhCesA4 in fiber development”has been published by theJournal of Advanced Research. In the paper,researchers from the Institute of Cotton Research (CCRI) report identified a gene that simultaneously regulates the negative correlation between cotton yield and fiber quality, via the linkage analysis between phenotypes and high-density genetic map using recombinant inbred lines of upland cotton.
Upland cotton is the world's largest natural fiber crop. Collaborative improvement of upland cotton yield and fiber quality has always been an important challenge in cotton breeding. Therefore, dissecting the genetic basis of the negative correlation between upland cotton yield and fiber quality, and identifying key genes for regulation, is of great significance.
In this study, through combined analysis of high-density genetic linkage maps, multi-environmental phenotype data and transcriptome study, GH_D07G2262 (cellulose synthase 4 gene, CesA4 ) was identified to simultaneously regulate the formation of fiber quality and yield traits. Preliminary functional validation was conducted through gene silencing (VIGS) and gene editing (CRISPR-Cas9) techniques, and the results showed that GH_D07G2262 gene positively regulates the formation of fiber strength, while negatively regulating the formation of lint percentage. These findings further elucidate the genetic basis for the negative correlation between fiber quality and yield in upland cotton, providing genetic resources for multi-trait collaborative improvement in upland cotton.
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070560, 32070563), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, the National Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project for Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2016-ICR), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (CN) (1610162023013), and the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2021D01B114), as well as the Talent Development Program for Innovation and Expansion in Xinjiang for Youlu Yuan Group.Ph.D. student Liu Ruixian is the first author of the paper. Prof. Yuan Youlu, Associate Prof. Gong Wankui from the Institute of Cotton Research and Professor Chen Quanjia from Xinjiang Agricultural University are the co-corresponding authors.
The article can be found: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2023.12.005
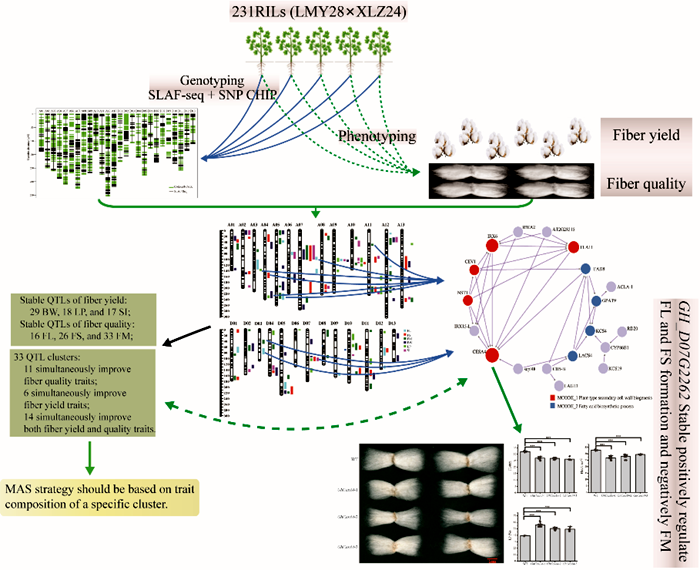
Fig 1. Functional studies on the gene GH_D07G2262
By Haoliang Yan (yanhaoliang@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
