Updated understanding of synchronously reducing arsenic and cadmium uptake by rice via the traditional ridge cultivation
Recently, the Remediation of Degraded and Contaminated Farmland Team from the Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, found that traditional ridge cultivation, coupled with fertilizer application, could synchronously curb arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice grains by enhancing the cascading effect of element cycling and key microbial functions. The related findings have been published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials.
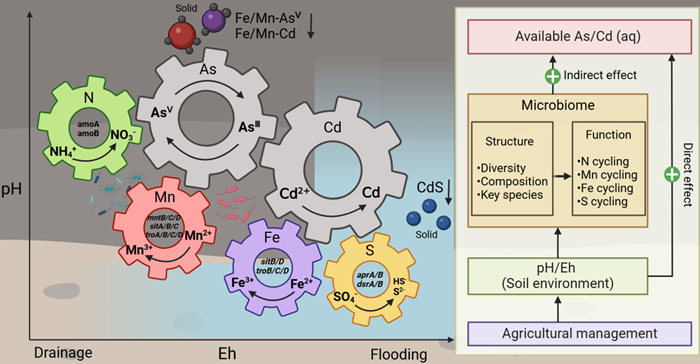
The co-contamination of As and Cd in rice fields threatens food security and human health, and synchronously remediating farmlands co-contaminated with Cd and As presents great challenges. Ridge cultivation in rice fields is a traditional agronomic measure for the improvement of cold waterlogged paddy fields in southern China. Ridge cultivation, in conjunction with reasonable fertilizer application, can synchronously prevent and control As and Cd accumulation in rice grains, and therefore ensure the safety of agricultural products. However, the microcosmic mechanism how the availability of soil As and Cd in rice fields varies under the regulation of this measure remains unclear.
The findings show that ridge cultivation in rice fields creates a new "semi-arid" habitat dominated by the cyclic coupling of iron, manganese and nitrogen, while applying calcium-magnesium-phosphate (CMP) fertilizers or biochar in ridged rice fields can synergistically reduce the bioavailability of Cd and As by enhancing the cyclic coupling of iron, manganese and nitrogen. The study also identified key microbial processes mediating the cyclic coupling of iron, manganese and nitrogen, and discovered the microbial predictors associated with lower bioavailability of Cd and As. This study provides theoretical support for technological innovations in green remediation of As and Cd co-contaminated rice fields in the future.
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science and the special fund for Science and Technology Innovation Teams of Shanxi Province.
Linkage: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.135244
-
 Aug 22, 2024Seminar on Grassland Protection and Sustainable Livestock Development for BRI Partner Countries has kicked off in Hohhot
Aug 22, 2024Seminar on Grassland Protection and Sustainable Livestock Development for BRI Partner Countries has kicked off in Hohhot -
 Aug 01, 2024Deputy Prime Minister of Cuba Visited IVF-CAAS
Aug 01, 2024Deputy Prime Minister of Cuba Visited IVF-CAAS -
 Aug 01, 2024CAAS Vice President Visits Africa
Aug 01, 2024CAAS Vice President Visits Africa -
 Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS
Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS -
 Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha
Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha
