New progress in the dissipation and potential risk of pesticide adjuvants in peanuts under different application modes
Recently, the Agro-product Quality and Safety Testing Technology Innovation Team from the Institute of Quality Standards and Testing Technology for Agro-Products of CAAS has revealed the dissipation behavior and potential risk of tristyrylphenol ethoxylate homologs (TSPEOs) in peanuts by spraying and root irrigation. Relevant results were published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials (IF: 13.6).
The study elucidated the residual dissipation behavior of different homologs TSPEOn under two application methods: spraying and root irrigation. The half-lives of TSPEOs residues in the root irrigation were significantly higher than that in the spraying. The half-lives of TSPEOn (n=1-29) in peanut plants and soil were 3.67-7.00 days and 5.41-8.15 days, respectively. The longer-chain TSPEOn (n=17-29) was more easily degraded in peanut plants. The residual concentrations of TSPEOs in peanut shells and soil through root irrigation were 1.0-4.8 times higher than those through spraying. Through dietary intake risk assessment and risk quotient methods, it was found that the health risks and ecological risks of TSPEOs residues in peanuts and soil were relatively low, but root irrigation might pose a higher potential risk than spraying. This study provides technical support for the rational use of pesticide adjuvant TSPEOs during peanut cultivation.
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricutural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-IQSTAP-02).
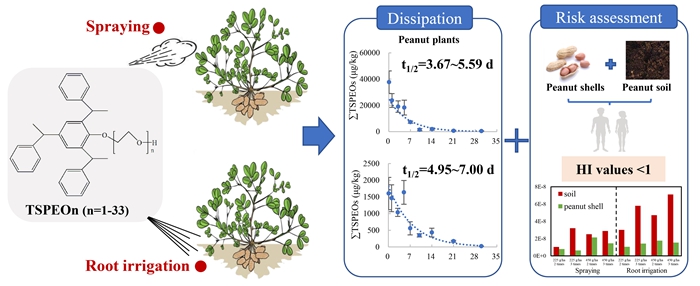
Figure 1 Comparison of dissipation and potential risks for TSPEOs in peanuts under different application methods
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134486
By Wang Hongping
(wanghongping@caas.cn)
-
 May 11, 2024WRI Deepens Agricultural Technology Cooperation with Agricultural Research Institutions in Uzbekistan
May 11, 2024WRI Deepens Agricultural Technology Cooperation with Agricultural Research Institutions in Uzbekistan -
 Apr 28, 2024CAAS President Meets President of Murdoch University
Apr 28, 2024CAAS President Meets President of Murdoch University -
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
