New progress in dissecting the population structure of cigar tobacco germplasm resources
Recently, the Center for Tobacco Genetics and Breeding of the Institute of Tobacco Research (TRI), Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences has made new progress in dissecting the population structure of cigar tobacco germplasm resources. The results were published in Industrial Crops and Products .
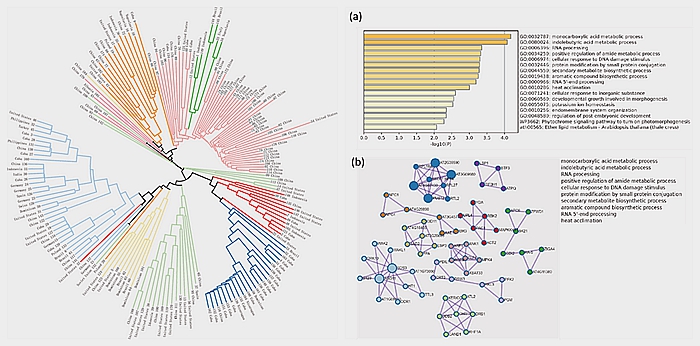
Cigar tobacco is an important economic crop, widely cultivated around the world. Its yield and quality are of great interests to tobacco researchers. Given that the genetic structure of cigar tobacco populations has not been revealed, this study conducted whole-genome resequencing of 185 cigar tobacco germplasm resources from 18 worldwide production regions. It obtained a Genome Variation Map (GVM) of cigar tobacco containing 2.12 million Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and analyzed its population structure and genetic diversity. Simultaneously, the field-based agronomic traits of this population were measured at two locations over three years, followed by the analysis of phenotypic diversity and heritability. Based on agronomic traits, a comparison between wrapper and filler populations was conducted, and the population differentiation between wrapper and filler was evaluated by combining genetic variation, exploring the impact of artificial domestication on the population structure of cigar tobacco. The research results indicate that as a result of modern breeding, significant phenotypic differences have emerged between wrapper and filler populations, with a beginning of differentiation in genetic structure, indicated by a differentiation coefficient of 0.16. Additionally, 1225 genes subject to domestication selection were identified through the selective sweep analysis. These genes are significantly enriched in biological processes such as monocarboxylic acid metabolism, indolebutyric acid metabolism, RNA processing, amide metabolism, cellular response to DNA damage stimulus, small protein modification, secondary metabolite synthesis, heat acclimation, cellular response to inorganic substances, and leaf development. This study preliminarily elucidates the molecular basis of population differentiation in modern cigar tobacco breeding, laying a theoretical foundation for development of cigar tobacco germplasm resources. This is crucial for the improvement of cigar tobacco breeding and other tobacco varieties.
The first author of the paper is a PhD student Xun Jiang from TRI. Jun Wang and Yanqing Qin from Sichuan Tobacco Company are co-first authors. Professor Peigang Dai, Associate Professor Xingwei Zhang, and Associate Professor Guoxiang Liu from TRI are co-corresponding authors of the paper. This research was supported by funding from Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, and Science and Technology Project of Sichuan Branch of China National Tobacco Corporation.
The article link is : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118153
By Liu Guoxiang (liuguoxiang@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
