Biochar made from waste straw can be used to repair cotton fields contaminated by residual film
Recently, a paper entitled “Exploring the potential of biochar for the remediation of microbial communities and element cycling in microplastic-contaminated soil” has been published by the Chemosphere. In the paper researchers from the Institute of Cotton Research (CCRI) report the mechanism of straw biochar in repairing soil contaminated by film-derived microplastics was discovered through microbial and elemental cycle analysis.
Existing studies have shown that microplastics have a negative impact on soil physicochemical, microbial and ecological functions, and residual film-derived microplastics have become an important factor restricting the green development of the cotton industry. The remediation effect of biochar on soil physicochemical and biological properties makes it a soil conditioner with broad application prospects, but the potential of biochar to repair residual film microplastic contaminated cotton fields is still unclear.
This study prepared two types of straw biochar using cotton and corn straw as raw materials. Through indoor co-cultivation, the mechanism of biochar repairing residual film-contaminated soil was explored from four aspects: microbial community, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus content, element cycle functional genes and functional microbial groups. The study found that the addition of biochar restored and strengthened the symbiotic network of soil microorganisms, increased the content of ammonium nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, available phosphorus and dissolved organic carbon in the soil, promoted the expression of genes related to the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus element cycle process, and increased the abundance of element cycle functional microorganisms. The results show that biochar plays an important role in reducing the adverse effects of soil microecology caused by residual film. The results provide theoretical support for the remediation of cotton fields contaminated by residual film.
This research was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1400300); Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences; China Agriculture Research System and Key Technologies R & D Program of Henan Province.Associate researcher Wu Changcai is the first author of the paper, and researchers Ma Yan and Cui Jinjie are the co-corresponding authors.
The article can be found:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142698
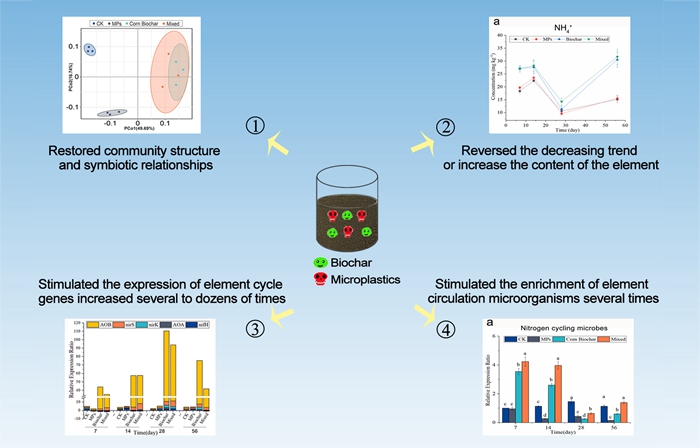
Fig 1.The mechanism of straw biochar in the remediation of soil contaminated by film-derived microplastics
By Changcai Wu (cczhacc@qq.com)
-
 Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS
Jul 16, 2024FAO Director-General Visits CAAS -
 Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha
Jul 16, 2024CAAS President Meets Vice Chancellor of University of Sargodha -
 Jul 11, 2024Dr. Liping Jin was awarded the "World Potato Industry Award"
Jul 11, 2024Dr. Liping Jin was awarded the "World Potato Industry Award" -
 Jul 11, 2024China-FAO Technical Training Workshop on FAW Monitoring and Forecasting
Jul 11, 2024China-FAO Technical Training Workshop on FAW Monitoring and Forecasting -
 Jul 08, 2024CAAS Delegation Visits Three European Countries for Multilateral and Bilateral Cooperation
Jul 08, 2024CAAS Delegation Visits Three European Countries for Multilateral and Bilateral Cooperation
