Scientists from IBFC CAAS Reveal the Anticancer Mechanism of Bioactive Peptide Lunasin
Recently, researchers from Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IBFC, CAAS) have revealed the molecular mechanism of lunasin on inhibiting the proliferation of human breast cancer cell of MDA-MB-231 by using multiple omics technology. This research provides theoretical support for the development and application of lunasin in anticancer products.
Lunasin is a bioactive peptide containing 44 amino acids, which was first isolated from soybean, and its content is about 0.6-3.2 g/kg. Lunasin contains an RGD cell adhesion module composed of Arg, Gly and Asp residues. Besides, its carboxyl terminus contains nine aspartic acid residues, which may play a decisive role in its physiological activity. Lunasin has been proved to exhibit several biological activities, including anti-inflammation, immune regulation, inducing apoptosis, anti-proliferation, etc. However, the molecular mechanism of lunasin on human breast cancer cells is still poorly understood.
In this study, synthesized lunasin was used, and its anti-proliferative activity was observed in MDA-MB-231 cells. Conjoint analysis of transcriptome and proteome was further performed. The results demonstrated that cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase (CASP) 3, CASP 7, and CASP 14 were significantly up-regulated after lunasin exposure, together with an increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio from 22.9 to 210.6, which indicated that caspase-mediated mitochondria intrinsic apoptosis was highly activated. Moreover, lysosomal pathway was significantly suppressed under lunasin exposure, suggesting that lysosome may cooperate with mitochondria to participate in apoptosis. In addition, lunasin also down-regulated genes involved in DNA replication in MDA-MB-231 cells. Overall, this study reveals that the anti-proliferation effect of lunasin peptide might be triggered via the inhibition of DNA replication and cell mitosis, as well as the promotion of lysosome-mitochondrial mediated cell apoptosis.
The research was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project of the CAAS.
The study entitled “Lunasin peptide promotes lysosome-mitochondrial mediated apoptosis and mitotic termination in MDA-MB-231 cells” has been published online in Food Science and Human Wellness and can be accessed through the following link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.06.018.
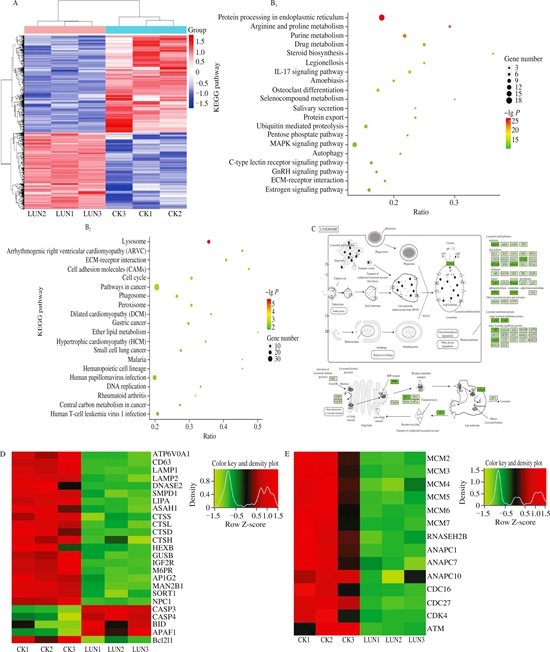
Fig. Proteomic analysis in MDA-MB- 231 cells
By Yang Xiushi(yangxiushi@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
