Researchers from IFST-CAAS Constructed the World's Largest Apple Temporal and Spatial Quality Evaluation Database
Apple is one of the most economically important fruit crops all over the world. Modern growers are keen to produce cultivars tailored to the apple industry that focuses on and cater to discern consumers, with changing preferences and dietary habits, who are highly aware of the nutritional and health benefits of fruits. Different varieties of fruit are different in edible quality, storage characteristics, nutritional quality, and other aspects, and fruit quality characteristics are directly related to metabolites. The establishment of a spatial-temporal quality evaluation database is the basis for improving fruit quality, which is not only to meet people's yearning for a better life but also an important measure for high-quality agricultural development, rural revitalization, and improvement of people's life and health.
Recently, researchers from Institute of Food Science and Technology (IFST), Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) established a spatio-temporal quality evaluation database of apples based on broad-spectrum metabolomics technology, including more than 2500 nutritional metabolites such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, organic acids, lipids, alkaloids, tannins, amino acids, nucleotides, sugars, sugar alcohols, and terpenoids. The quality and metabolite content of 292 apple accessions from all over the world were analyzed. The metabolites and nutritional characteristics of different pedigrees were compared, and the effects of characteristic metabolites on fresh eating, processing, and storage of different fruits were identified. On this basis, whole genome sequencing was carried out for apple accessions, and the regulatory loci of fruit nutritional quality metabolites was analyzed based on whole-genome association analysis, and the loci significantly associated with apple nutritional metabolites were identified. At present, this database is the largest temporal and spatial quality evaluation database of apple in the world. It systematically analyzes the regulatory sites of metabolite metabolism from the whole genome level, providing data support for the improvement, processing suitability and nutritional quality evaluation of fruit, and will greatly promote the digitalization and identification of fruit quality, and the specialization of raw material varieties. It provides technical support for building the brand of fruits and promoting standardization of processing.
This research was published in the top journal Genome Biology (IF5-y="20.366)." Dr. Qiong Lin, Ms Jing Chen, Dr. Xuan Liu from IFST-CAAS, and Dr. Bin Wang from Wuhan Metware Biotechnology Co., Ltd. are the co-first authors. The corresponding author is Prof. Jinfeng Bi from IFST-CAAS. The research materials are collected from the National Repository of Apple and Pear Germplasm Resources. This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD2100100), the earmarked fund for the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-27), the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of IFST-CAAS (CAAS-ASTIP-G2022-IFST-02), and the China Scholarship Council (201903250033).
Link to the paper:
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-023-02945-6
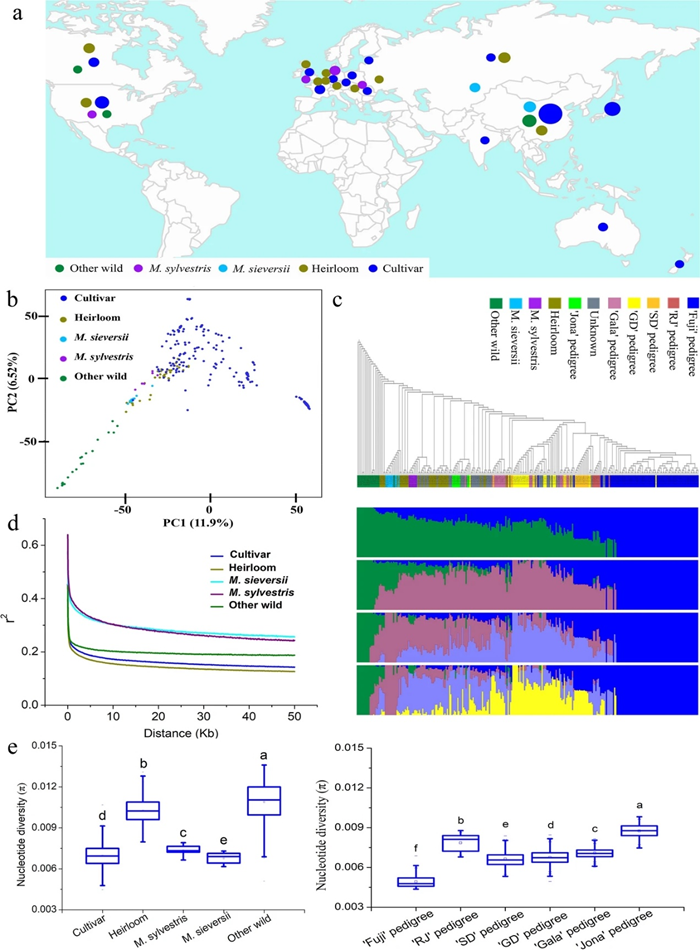
Figure. Genome-wide relationship in cultivated apple and wild species
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
