Salt induced “cry for help” to recruit root-associated Pseudomonas in wild soybean
Recently, the Evaluation and Utilization of Biological Resources in Coastal Saline-alkali Land Team from the Institute of Tobacco Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences has made important progress, revealing the salt-tolerant legume wild soybean recruits beneficial microbial taxa to resist salt stress by secreting key metabolites. The related findings have been published in Nature Communications .
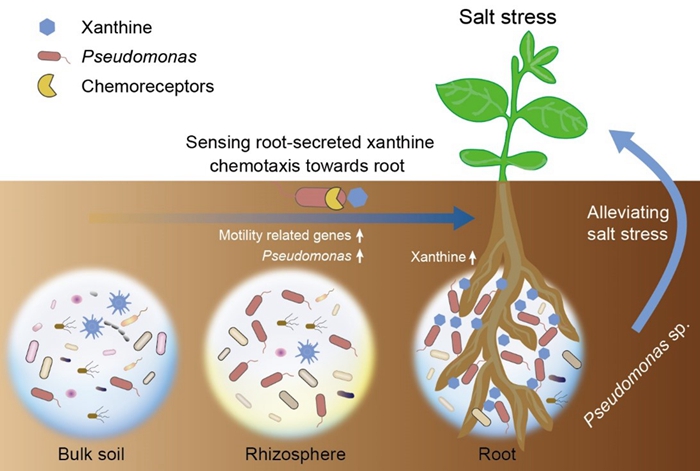
Saline-alkali land is an important reserved cropland resources in China. The steady development of soybean cultivation in saline-alkali land is of significance for guaranteeing national food security. In fact, cultivated soybeans are generally salt-sensitive, whereas their wild relatives, wild soybean, show high tolerance to salt. The plant microbiome plays an important role in response to biotic and abiotic stresses, and has been considered as the second genome of plant. However, how the salt-tolerant plant wild soybean shapes root-associated microbial community to enhance salt tolerance remains unclear.
This study focused on the microbiome of wild soybean, and found that under salt stress, wild soybean reshaped root-associated microbiota by secreting purines to recruit Pseudomonas . The researchers further conducted Pseudomonas mutant analysis, and demonstrated that motility related gene cheW was required for chemotaxis toward xanthine and for enhancing plant salt tolerance. This study firstly clarified the process and mechanism of salt-induced “cry for help”, which provided scientific basis for the utilization of beneficial microbes to improve soybean production in saline-alkali land.
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation.
linkage: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47773-9
By Zheng Yanfen(zhengyanfen@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 28, 2024CAAS President Meets President of Murdoch University
Apr 28, 2024CAAS President Meets President of Murdoch University -
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
