CAAS Scientists Make Progress on Genetic Mechanism of Water Loss in Rice
The global problem of drought threatens agricultural production and constrains the development of sustainable agricultural practices. In plants, excessive water loss causes drought stress and induces early senescence. Severe water shortages restrict the expansion of rice production and hinder the irrigation of existing paddy fields. Recently, scientists from China National Rice Research Institute (CNRRI) of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) have made progress on genetic mechanism of water loss in rice.
In this study, CAAS scientists isolated a rice (Oryza sativa.L) mutant, designated as early senescence 1 (es1-1), which exhibits early leaf senescence. The es1-1 leaves undergo water loss at the seedling stage (as reflected by whitening of the leaf margin and wilting) and display early senescence at the three-leaf stage. ES1 was cloned using map-based strategy, which encodes a SCAR-like protein 2, a component of the SCAR/WAVE complex involved in actin polymerization and function. Moreover, es1-1 mutants exhibited significantly higher stomatal density.
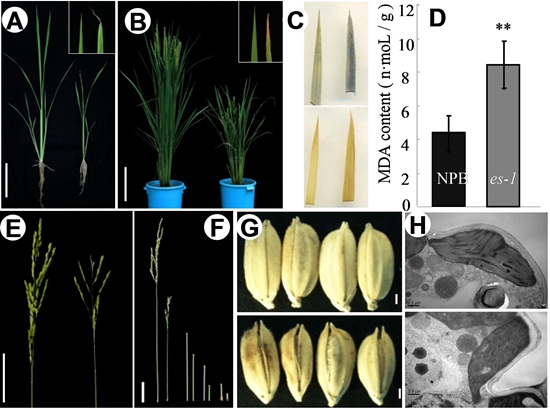
Phenotypes of wild-type and es1-1 plants
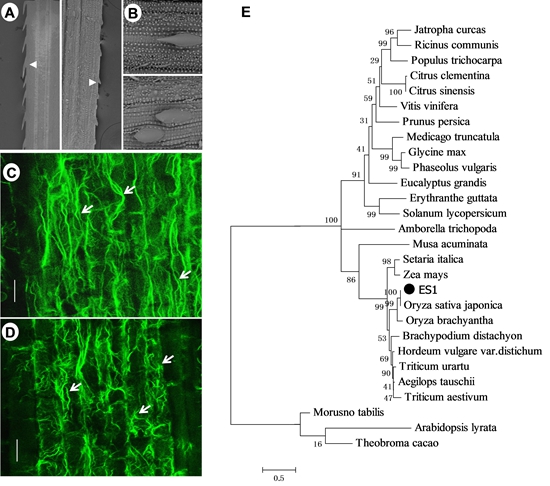
ES1 is a SCAR homolog
-
 Mar 21, 2025Experts from IPPCAAS Implement FAO-China South-South Cooperation Project to Advance Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management in Ghana
Mar 21, 2025Experts from IPPCAAS Implement FAO-China South-South Cooperation Project to Advance Sustainable Fall Armyworm Management in Ghana -
 Mar 13, 2025CAAS and CGIAR Deepen Strategic Cooperation
Mar 13, 2025CAAS and CGIAR Deepen Strategic Cooperation -
 Mar 11, 2025Call for Logo Design Proposals for the China-Africa Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance (CAASTIA)
Mar 11, 2025Call for Logo Design Proposals for the China-Africa Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance (CAASTIA) -
 Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation
Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation -
 Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
