Experts from the Institute of Pomology revealed the mechanism of phenolic metabolism regulated by melatonin in pear peel
Recently, the research group of Cheng cungang from the Institute of Pomology of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IP, CAAS), published a research paper titled "Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal phenolic metabolism regulated by melatonin in pear peel" in the JCR Q1 journal, (IF2024=5.2). The paper revealed how melatonin regulates the metabolism of phenolic substances in pear peel.
Melatonin is a crucial regulator of fruit growth and development. The previous research has shown that pre-harvest application of melatonin can affect phenolic metabolism to improve the color, strength, and antioxidant capacity of pear peels. However, the mechanisms by which pre-harvest application of melatonin regulates the metabolism of phenolic compounds in pear pericarp remain poorly understood.
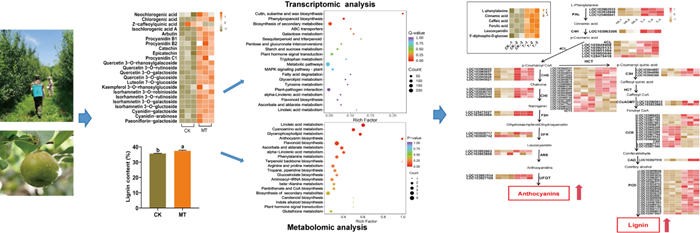
In this study, the research group used a multi-disciplinary approach, integrating physiological and biochemical, transcriptomic, and metabolic analyses, to elucidate the pre-harvest application of 100 μM melatonin can influence the key enzyme genes' expression in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and flavonoid biosynthesis pathways, while stimulating the production of L-phenylalanine, cinnamic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, leucocyanidin and uridine 5ʹ-diphospho-D-glucose, which promote the biosynthesis of anthocyanidins, phenolic acids, and lignins. Moreover, by examining the expression patterns of transcription factors, the research group identified 12 potential key TFs involved in melatonin-regulated polyphenol biosynthesis. These findings provide comprehensive insights into the metabolic mechanisms of melatonin-regulated phenolic compounds in pear peels.
Professor Cheng cungang of Institute of Pomology and Professor Zhou Zhiqin of Southwest University are the corresponding author of the paper. Dr. Yan Shuai and Zhao Liangliang are the co-first authors. This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD1600503); Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2021-RIP-03) and Key Research and Development Program of Shandong (2022LZGC011).
Link: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-025-00763-5
By: Shuai Yan
(yanshuai@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 25, 2025CAAS President Meets Director General of IAEA
Apr 25, 2025CAAS President Meets Director General of IAEA -
 Apr 25, 2025CAAS Delegation Attends CGIAR Science Week 2025
Apr 25, 2025CAAS Delegation Attends CGIAR Science Week 2025 -
 Apr 25, 2025Delegation Led by CEO of Punjab Agricultural Research Council Abid Mahmood and Vice Dean of PKU Advanced Agricultural Research Institute Zhang Xingping Visits Shouguang R&D Center of CAAS
Apr 25, 2025Delegation Led by CEO of Punjab Agricultural Research Council Abid Mahmood and Vice Dean of PKU Advanced Agricultural Research Institute Zhang Xingping Visits Shouguang R&D Center of CAAS -
 Apr 11, 2025Strengthening China-Mongolia Grassland Cooperation to Build a Cross-Border Green Ecological Barrier
Apr 11, 2025Strengthening China-Mongolia Grassland Cooperation to Build a Cross-Border Green Ecological Barrier -
 Apr 03, 2025CAAS and CABI Forge a New Chapter in Strategic Cooperation
Apr 03, 2025CAAS and CABI Forge a New Chapter in Strategic Cooperation
