IPPCAAS Successfully Elucidates the Transformation Processes and Environmental Risks of Dufulin in Aquatic Environments
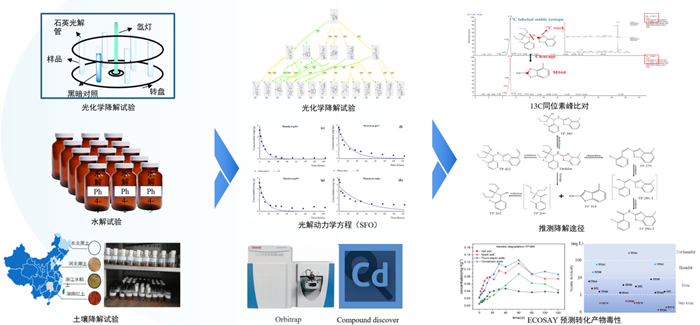
Recently, the Innovation Team for Risk Control of Pesticide Application at the Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IPPCAAS) has successfully elucidated the transformation pathways and environmental risks of the domestically developed pesticide Dufulin in aquatic environments. Using 13C stable isotope labeling coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrum (HRMS), the team identified the major transformation products (TPs) of Dufulin and assessed their potential ecotoxicity using the ECOSAR model. The findings, published in the top environmental journal Water Research , provide crucial insights into pesticide degradation mechanisms, unknown TPs identification, and environmental risk assessment.
Dufulin, an efficient antiviral agent for plants, has been widely used in agricultural production. However, its environmental fate, particularly the formation and non-target toxicity of TPs, remains unclear. In aquatic environments, Dufulin undergoes abiotic degaradation, generating TPs that may pose greater ecological risks than the parent compound. Therefore, it is critical to investigate the environmental behaviour of Dufulin and the identification and risk evaluation of corresponding TPs.
This study investigated the degradation behaviour of Dufulin in aquatic environments and described its photolysis and hydrolysis processes using different kinetic models. The Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Exactive-MS) coupled with 13C stable isotope labeling was utilized to comprehensively identify and quantify Dufulin and its TPs for the first time. A total of six TPs were identified and confirmed, among which five were newly discovered. It further proposed that the main non-biological pathways of Dufulin in water include reductive cleavage, oxidation, elimination, and deethylation, which provided theoretical support for a deeper understanding of its environmental fate. Additionally, the ECOSAR model assessment revealed that two of these TPs may exhibit higher ecological toxicity to zebrafish, Daphnia magna, and green algae might be higher than that of the parent compound. This finding holds significant implications for the environmental risk assessment of Dufulin.
This research has made a breakthrough in the methodology for screening and identifying unknown TPs of pesticides using 13C stable isotope labeling. This approach enables structural confirmation of potential transformation products without the need for standard comparison, effectively solving the problem of pesticide TPs identification. It significantly enhances the efficiency of unknown compound identification and provides a valuable reference for the identification and toxicity risk assessment of other pesticide TPs.
IPPCAAS is the leading institution of this study. Dr. Yu Bochi is the first author, and Professor Liu Xiangang is the corresponding author. This study was supported by the International (Regional) Cooperation and Exchange (ICE) Projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.32261133527).
Links:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123150
-
 Mar 13, 2025CAAS and CGIAR Deepen Strategic Cooperation
Mar 13, 2025CAAS and CGIAR Deepen Strategic Cooperation -
 Mar 11, 2025Call for Logo Design Proposals for the China-Africa Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance (CAASTIA)
Mar 11, 2025Call for Logo Design Proposals for the China-Africa Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Alliance (CAASTIA) -
 Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation
Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation -
 Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland -
 Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS
Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS
