Researchers reveal a new mechanism by which baicalin alleviates bacterial intestinal inflammation in piglets
Recently, a study conducted by the Animal Nutrition and Regulation Innovation Team, Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, has revealed that baicalin alleviates bacterial intestinal inflammation in piglets by regulating macrophage polarization and promoting the colonization of Lactobacillus amylovorus . This work elucidates the effects and underlying mechanisms of baicalin and provides important theoretical support for the development of novel feed additives based on the natural plant-derived compound baicalin and probiotics. The findings were published in Advanced Science .
Piglets are particularly vulnerable to pathogenic infections such as Escherichia coli , especially during the weaning stress period, due to their immature intestinal development. These infections often lead to intestinal inflammation and diarrhea. Scutellaria baicalensis , a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, is known for its antimalarial and antidiarrheal properties; however, the anti-inflammatory and antibacterial mechanisms of its main active compound, baicalin, remain unclear.
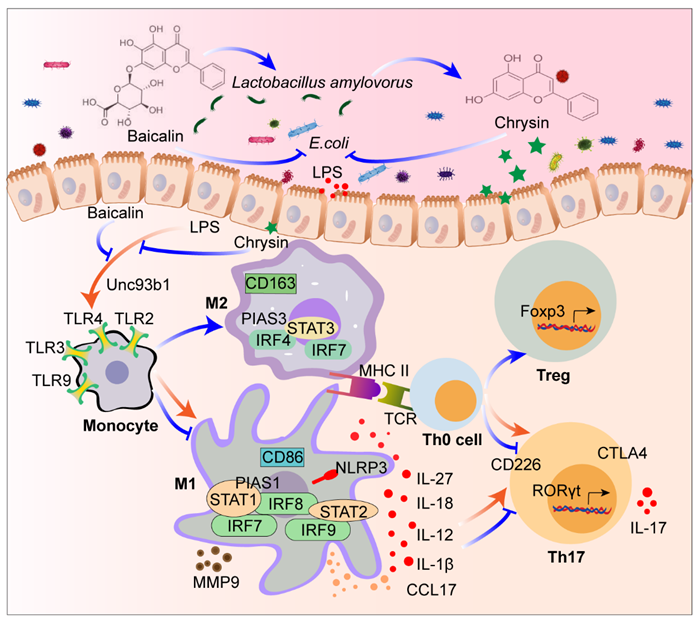
This study found that baicalin significantly improved colonic morphological damage in piglets caused by Escherichia coli and regulated the expression of genes related to Th17 cell differentiation. Further studies have revealed that baicalin can inhibit the polarization of M1-type macrophages through the TLR4/IRF/STAT pathway, thereby suppressing the intestinal inflammatory response. Based on the analysis of the intestinal microbiome and metabolomics, it was discovered for the first time that baicalin upregulated the abundance of Lactobacillus amylovorus in the colon of piglets and increased the levels of key metabolites such as chrysin, lactic acid and indole. A novel strain of Lactobacillus amylovorus SKLAN202301ZF was successfully isolated from the colon of piglets in the study. The effect of this strain and its key metabolite, chrysin, in alleviating intestinal inflammation caused by Escherichia coli via inhibiting the polarization of M1-type macrophages was verified. This study clarified the mechanism of baicalin, an active component of traditional Chinese medicine, in synergistically alleviating bacterial enteritis with Lactobacillus amylovorus , providing theoretical support for the development of feed additives to maintain the intestinal health of piglets and facilitating the research and development of new products with natural functional components of Chinese herbal medicine.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth innovation of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program.
Article link:
https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202415948
By Zhong Ruqing (zhongruqing@caas.cn)
-
 May 18, 2025Sustainable Dairy Development — The 9th International Symposium on Dairy Cow Nutrition and Milk Quality Convenes in Beijing
May 18, 2025Sustainable Dairy Development — The 9th International Symposium on Dairy Cow Nutrition and Milk Quality Convenes in Beijing -
 Apr 25, 2025CAAS President Meets Director General of IAEA
Apr 25, 2025CAAS President Meets Director General of IAEA -
 Apr 25, 2025CAAS Delegation Attends CGIAR Science Week 2025
Apr 25, 2025CAAS Delegation Attends CGIAR Science Week 2025 -
 Apr 25, 2025Delegation Led by CEO of Punjab Agricultural Research Council Abid Mahmood and Vice Dean of PKU Advanced Agricultural Research Institute Zhang Xingping Visits Shouguang R&D Center of CAAS
Apr 25, 2025Delegation Led by CEO of Punjab Agricultural Research Council Abid Mahmood and Vice Dean of PKU Advanced Agricultural Research Institute Zhang Xingping Visits Shouguang R&D Center of CAAS -
 Apr 11, 2025Strengthening China-Mongolia Grassland Cooperation to Build a Cross-Border Green Ecological Barrier
Apr 11, 2025Strengthening China-Mongolia Grassland Cooperation to Build a Cross-Border Green Ecological Barrier
