Bacillus velezensis solid-state fermentation product improved the hepatointestinal health of common carp ( Cyprinus carpio )
Recently, the Aqua-Microbiome and Feed Research Team from the Institute of Feed Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences revealed the beneficial effects of Bacillus velezensis T23 solid-state fermentation product on growth, gut and liver health, and gut microbiota homeostasis of common carp. The related findings have been published in Aquaculture journal.
To address the issue of excessive antibiotic use in intensive aquaculture, many are turning to environmentally friendly probiotics as a primary alternative, with Bacillus spp. being the most commonly utilized. However, there is limited documentation on the use of cost-effective and high-yield probiotic solid fermentation as additives in aquaculture. To assess the effect of solid fermentation on liver and intestinal health in fish, the0, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4 g/kg solid statefermentation product of Bacillus velezensis T23 supplemented diets (39% crude protein and 10% crude fat)wereevaluated. Dietary 0.3 and 0.4 g/kg supplementationof Bacillus velezensis T23 solid-state fermentation productspromoted lipolysis and inhibited lipid synthesis. Meanwhile, the intestinal microbiota health index "(Fusobacteria + Firmicutes + Bacteroidetes)/ Proteobacteria" was significantly increased in 0.3 and 0.4 g/kg supplementation groups. Furthermore, 0.3g/kg supplementation inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory genes and up-regulated the expression of anti-inflammatory genes, and could increase the α-diversity of intestinal microorganisms and the relative abundance of Fusobacteria and Cetobacteria . The Bacillus velezensis T23 may play a key role in maintaining a balanced intestinal microbiota via increasing the proportion of beneficial bacteria, and itmay promote fat decomposition and inhibit fat synthesis through Cetobacteria with lipid-lowering function. These findings provided a novel insight into the solid fermentation products reducingthe lipid accumulation of carp and provided data reference for industrial applications, which provided theoretical reference and data support for the practical application of probiotics in aquaculture.
This research was supported by theNational Key Research and DevelopmentProgram of China(2022YFC2105005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 32330110, 31925038, 32172991, 32202959, 32172958, 32122088,32102812 and U21A20267), Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ZDRW202305 and CAAS-ASTIP-2023-IFR-05), Beijing Innovation Consortium of Agriculture Research System (CSC No. 202203250030), China Scholarship Council (CSC) under the State Scholarship Fund and the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (GZB20230856).
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741733
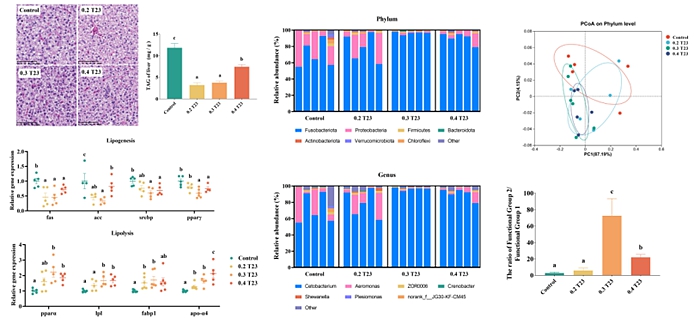
Figure. Effects of Bacillus velezensis T23 solid-state fermentation product on liver and intestine health of Cyprinus carpio
By Xingyu Chen, 1525934724@qq.com
Shubin Liu, liu609801601@vip.qq.com
-
 Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation
Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation -
 Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland -
 Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS
Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS -
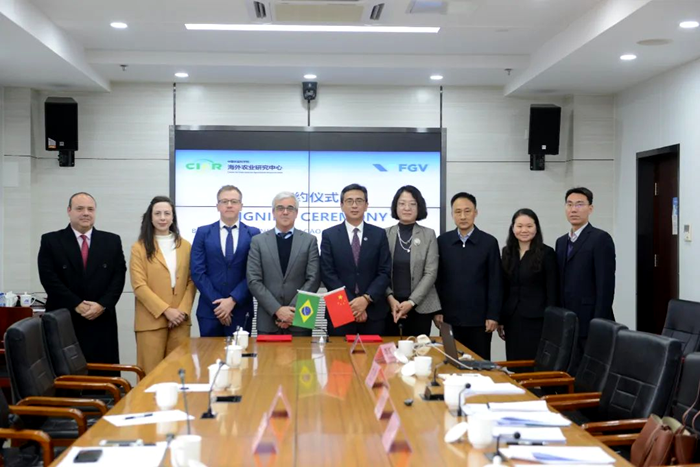 Dec 05, 2024CIAR and FGV Deepen Cooperation to Promote the Development of China-Brazil Green Agricultural Products Value Chain
Dec 05, 2024CIAR and FGV Deepen Cooperation to Promote the Development of China-Brazil Green Agricultural Products Value Chain -
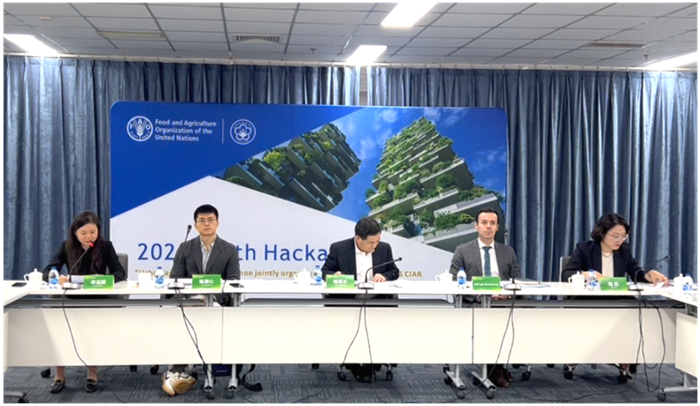 Dec 05, 20242024 Youth Hackathon for Urban Agriculture Finals Successfully Held in Beijing
Dec 05, 20242024 Youth Hackathon for Urban Agriculture Finals Successfully Held in Beijing
