-
Oct 23 2015
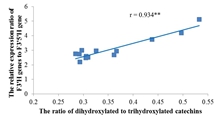
New advance in the regulation system of catechin composition in Camellia sinensis
The ratio of dihydroxylated to trihydroxylated catechins (RDTC) is an important indicator of tea quality and biochemical marker for the study of genetic diversity. -
Sep 21 2015

Researchers reveal a dominant QTL to enhance rice grain size and grain yield
Grain size determines grain weight and affects grain quality. Several major quantitative trait loci (QTLs) regulating grain size have been cloned while our understanding of the underlying mechanism on... -
Sep 18 2015
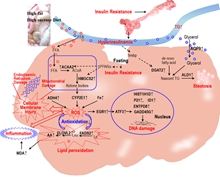
Energy supply shifted from glucose to ketone bodies trigger the NASH in early stage by minipigs model
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a burgeoning global health problem and includes a disease spectrum ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hep... -
Sep 09 2015
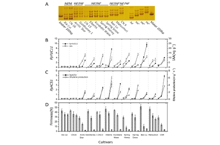
New Research Progress on Genetic Mechanism of Stony Hard Phenotype in Peach
Prompt post-harvest softening of fruits is one of the major bottleneck constraints of peach industry development. Therefore, the study of fruit maturation and softening mechanism of peach is of great ... -
Sep 09 2015

CAAS VP made presentation to the Standing Committee Members of 12th CPPCC National Committee
On August 28, during the 12th working session of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) held in Beijing. -
Sep 08 2015
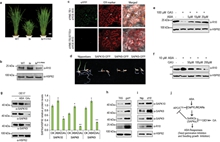
Antagonism Mechanism of GA on ABA signaling pathway
ABA is a stress responsive phytohormone which inhibits seed germination and seedling growth to adapt to unfavorable environmental conditions while GA is a major growth promoting phytohormone which pro... -
Aug 27 2015
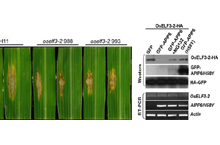
OsELF3-2, an ortholog of Arabidopsis ELF3, interacts with the E3 ligase APIP6 and negatively regulates immunity against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice
Rice blast, which is caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae, significantly reduces rice yield in most rice-growing areas. -
Aug 27 2015
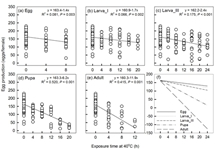
Heat waves occurred in different life-stages contribute differently in survival and reproduction of a global pest, the diamondback moth
Global climate change will not only lead to a substantial increase in average temperature but also in the frequency and duration of hot events. -
Aug 25 2015
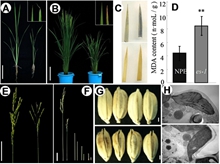
CAAS Scientists Make Progress on Genetic Mechanism of Water Loss in Rice
The global problem of drought threatens agricultural production and constrains the development of sustainable agricultural practices. In plants, excessive water loss causes drought stress and induces ... -
Aug 25 2015
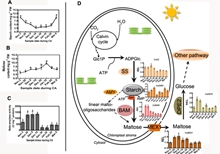
CAAS Researchers Reveals Effects of Cold Acclimation on Sugar Metabolism and Sugar-related Gene Expression in Tea Plant during the Winter Season
Tea plant (Camellia sinensis) is a temperate woody plant, whose leaves are consumed as a beverage around the world, and is susceptible to low temperature. It’s growth and geographical distribution are...
